
Expenses are matched to the period when revenue is generated as a direct result of using that asset. Depreciation and Amortization are two ways to ascertain asset value over a period of their useful life. We’re going to all break it down for you and help you understand the differences between depreciation and amortization.

Company Overview
These are initial costs paid by a company and are usually paid upfront. The depletion method is used by companies extracting natural resources like oil, gas, minerals, and metals. Depreciation is calculated by subtracting the asset’s resale value from its original cost.
- The amortization of a loan is defined as the gradual reduction in the loan principal via periodic, scheduled payments to the lender, such as a bank.
- Depreciation and amortization, while sharing the common goal of allocating asset costs over time, serve distinct purposes for tangible and intangible assets, respectively.
- The useful life of the patent for accounting purposes is deemed to be 5 years.
- For instance, the recorded value of a company’s inventory, a current asset, can be written down partially on the books or completely wiped out based on the estimated fair value.
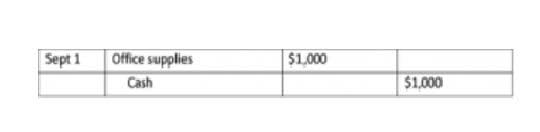
- For example, when you buy a car or any type of fixed asset, you capitalize it and you don’t expense it, and it goes on your balance sheet.
- Here, the term “amortization schedule” means a payment schedule, each including part of the debt and interest accrued.
AccountingTools

Tangible assets are physical items with a finite lifespan, such as machinery, vehicles, buildings, Suspense Account and equipment. The rationale behind depreciation is to match the cost of these assets with the revenue they generate over time. As amortization directly affects a company’s reported net income, it is an extremely important component for investors to evaluate. New rules for generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require intangible asset values to be re-evaluated at least annually. If the fair value is determined to be less than the intangible asset’s current valuation minus the amortization expense, the asset is said to be impaired.
Regulatory Standards: Accounting Principles
Used correctly, they can reduce your tax bill and improve cash flow. Used incorrectly, they can cause financial issues and even attract IRS attention. Consider a scenario where you purchase a delivery van for your company. Most small businesses use the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), which allows you to deduct more in the early years, benefiting cash flow.
It recognizes the gradual wear and tear or obsolescence of these assets and spreads their costs across multiple accounting periods. Depreciation reflects the decrease in an asset’s value as it ages and undergoes usage, deterioration, or technological advancements. With so many variables and inferences involved with determining amortization and the life expectancy of an intangible asset, impairment cost can be used to manipulate the balance sheet. One of the main factors contributing to manipulation is the fact that declared values of intangible assets are not required to be reported. Amortization and depreciation when preparing the income statement are treated as non-cash transactions. These concepts are introduced because they simplify capital expenditure planning.
- For this reason, overstating or understating the asset’s salvage value and useful life can make quite an impact on the company’s bottom line.
- The difference is depreciated evenly over the years of the expected life of the asset.
- Amortization is typically expensed on a straight-line basis, meaning the same amount is expensed in each period over the asset’s useful lifecycle.
- Amortization is similar to depreciation in that it’s used to spread the cost of an asset over a period of time.
- Understanding the differences between these methods is crucial for effective asset management and tax planning in your business.
On the other hand, due to the yearly amortization of assets, the balance sheet is affected as it reduces the asset side of amortization vs depreciation the statement. The way cost is allocated when using these two concepts can also vary. Amortization almost always follows a straight-line approach, meaning the cost is evenly spread across the asset’s useful life. Recognizing the tax implications of depreciation and amortization is vital for your business as they can significantly affect your taxable income.

For instance, a business owner would want to know the differences between amortization and depreciation because of how it can impact tax liability and the financial statements of their business. Both amortization and depreciation involve recognizing expenses over time. Companies spread the cost of an asset across its useful life, rather than expensing it all at once. This approach aligns the expense with the revenue generated by the asset, providing a more accurate picture of financial performance. Depreciation is used for tangible assets, or physical assets, like buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles, and furniture. These assets wear down over time due to physical use and are depreciated to reflect this decrease in value.
- To aid your understanding of both methods, here are their similarities.
- Under the straight-line method, the annual amortization expense is $10,000, reducing the book value of the patent during this time, thereby capturing its reduced economic benefit.
- The business then expenses a portion of the asset by using a numerator that represents each of those years.
- Depreciation and amortization are both accounting methods used to spread the cost of an asset over its useful life, but they apply to different types of assets.
- Both are non-cash expenses but play a crucial role in providing a realistic view of your business’s profitability and financial health.
- Both amortization and depreciation are non-cash expenses because they do not involve actual cash outflows during the period.
- They determine this number based on their understanding of printer technology trends.
Let’s say that you purchase a $50,000 piece of equipment to manufacture branded coffee mugs. The particular model you buy is expected to produce 50,000 mugs during its useful life. Following that, your number cruncher then deducts $5,000 from the cost of the equipment for 2022. This brings your net profit down to $95,000, which is not that significant of a difference. Explanations may also be supplied in the footnotes, particularly if there is a large swing in the depreciation, depletion, and amortization (DD&A) petty cash charge from one period to the next. The cost depletion method will require calculating the total resource endowment.
